| Trees | Indices | Help |
|
|---|
|
|

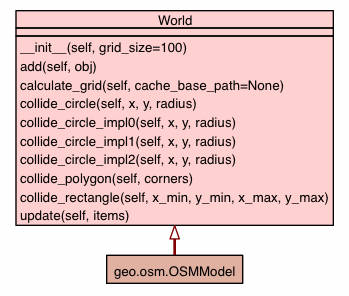
A set of all walkable elements in the simulated world, e. g. streets and public places.
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
Inherited from |
|||
|
|||
|
Inherited from |
|||
|
|||
Initialize collision grid. grid_size determines maximum collision region. Collision range/region/radius must be lower or equal the grid_size. World.obj is the set of walkable elements. calculate_grid() must be called after all objects have been loaded.
|
Calculates the collision grid of the World. This method must be called after all world objects have been added to the World. It calculate which objects are in which grid segment. Calculation is done by colliding each object with each grid segment. Determining a grid grid segment by coordinates is done by integer maths. A grid segment is represented by its west and south border, e.g. grid_size=50, p=(127.9; 33.2) => segment is x=100, y=0. |
Checks all registered walkable objects for collision that are in grid segments which collide with the specified circle. This method first determines all concerned grid segments and finally only collides objects located in these segments. This implementation uses Line.collide to determine neighbor segments by colliding circle with segment boundaries. |
Checks all registered walkable objects for a collision with a given circle. Simplest implementation, least performance. |
Checks all registered walkable objects for collision that are in grid segments which collide with the specified circle. This method first determines all concerned grid segments and finally only collides objects located in these segments. This implementation uses sub/add/abs to determine neighbor segments by checking coordinates. |
Checks all registered walkable objects for collision that are in grid segments which collide with the specified circle. This method first determines all concerned grid segments and finally only collides objects located in these segments. This implementation uses Line.collide to determine neighbor segments by colliding circle with segment boundaries. |
Checks all registered walkable objects for a collision with a given polygon. Status: not implemented |
| Trees | Indices | Help |
|
|---|
| Generated by Epydoc 3.0.1 on Sun Jul 6 13:59:48 2014 | http://epydoc.sourceforge.net |